Several international human rights agreements protect children from child marriage, including the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948), the Convention of Eradication of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women (1979), the Convention on the Rights of the Child (1989), and the African Charter on the Rights and Welfare of the Child (1990). All call for the free and full consent of both parties to marriage, a minimum age of marriage of 18, designation of child marriage as a harmful practice, and protection for the rights of children from all forms of exploitation.1
Early marriage compromises girls’ development and often results in early pregnancy and social isolation. Child marriage also reinforces the vicious cycle of early marriage, low education, high fertility, and poverty. Setting and enforcing a minimum legal age for marriage is necessary to protect girls, who are more affected than boys by the practice of child marriage. Most countries in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region have laws on the minimum age for marriage, ranging from age 13 in Iran to age 20 in Tunisia for females, and from age 15 in Yemen to age 21 in Algeria for males (see table).
Minimum Legal Age for Marriage in the Middle East and North Africa
Country Female Male Algeria 18 21 Egypt 16 18 Iran 13 15 Iraq 18 18 Jordan 18 18 Morocco 18 18 Tunisia 20 20 Yemen 15 15
Source: UNdata, “Minimum Legal Age for Marriage Without Consent” (http://data.un.org/Data.aspx?q=marriage&d=GenderStat&f=inID:19, accessed Feb. 18, 2010).
Some families take advantage of religious laws that condone an earlier marriage age, and arrange for their daughters to marry in religious wedding ceremonies, postponing the official registration until the bride reaches the legal age. Such practices further disadvantage child brides, leaving them with no legal basis to receive inheritance, alimony, or child support if the husband dies prematurely or abandons his underage bride.
With many families conducting religious ceremonies to marry off their young daughters and a low minimum legal age for girls in some countries, a significant number of girls in the MENA region still get married before age 18. In Yemen, one-third of women ages 20 to 24 are married by age 18. In Palestine, Egypt, and Iraq, significant proportions of women ages 20 to 24 were married before their 18th birthday (see figure). Among countries with available data, Algeria has the lowest percent of young women who were married before their 18th birthday, 2 percent.
Percent of Women Ages 20 to 24 Married Before Age 18
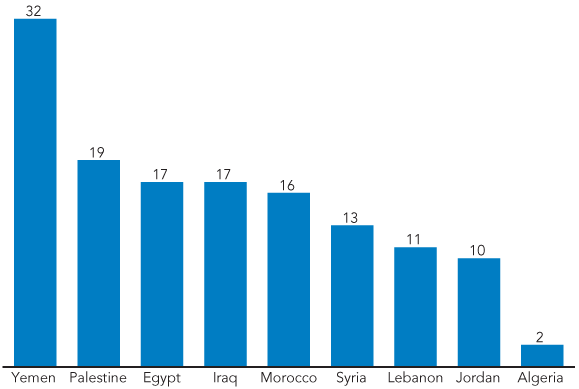 Source: UNICEF, Child Info: Monitoring the Situation of Children and Women (www.childinfo.org/marriage_countrydata.php, accessed Feb 18, 2010).
Source: UNICEF, Child Info: Monitoring the Situation of Children and Women (www.childinfo.org/marriage_countrydata.php, accessed Feb 18, 2010).
The Best Defense: Keep Girls in School
Education is the most important factor influencing the age of marriage for women. Improving access to education for both girls and boys and eliminating gender gaps in education are important strategies for ending child marriage. Since families have great influence in their daughters’ marriages, they need to be involved in the solution and encourage their daughters to stay in school and ensure a protected transition to adulthood.
Increasing the years of compulsory education may be one tactic to prolong the period of time when a girl is in school and unavailable for marriage. In addition, policies and programs should be geared toward discouraging early marriage by:
- Encouraging parents to keep their daughters in school until they finish high school and subsidizing the cost for families with limited financial resources.
- Raising public awareness about children’s rights to education and protection against exploitation.
- Changing the attitudes of people who condone the practice of early marriage by targeted campaigns and use of the mass media, showcasing the benefits of keeping girls in school for their individual development and well-being, as well as for benefits to their families.
Reaching Out to Young Married Women
Girls who marry young are at a higher risk of domestic violence and sexually transmitted diseases, especially since sex is likely to be unprotected within marriage.2 Social norms often dictate that these young women produce children as soon as possible after marriage, but girls are risking their lives in doing so—young adolescents’ risk of illness, injury, or death as a result of pregnancy is much higher than for women over 18.3
Efforts are also needed to address concerns of those who are already married at a young age by:
- Ensuring their access to school, so they can fulfill their right to a full education.
- Decreasing the pressure on young women to conceive through advocacy and education on the dangers of early motherhood.
- Improving their access to reproductive health care, including family planning services.
- Providing them with training programs to improve their life skills and ensure that they can earn a livelihood.
- Providing services to victims of domestic violence.
The Role of Mass Media
The media can also play a key role in bringing the issue of child marriage to public attention. Journalists can use current data to inform human rights advocates and policymakers of the negative aspects of child marriage by covering the issue from multiple perspectives—the illegal violation of girls’ human rights, the mental and physical harm on girls’ development, and the negative consequences for families and societies.
The media can force policymakers to react, as happened in highly publicized cases in Yemen and Saudi Arabia where girls as young as 9 and 12 were trying to divorce their older husbands. In both countries, the publicized cases brought child and human rights advocates and lawyers together to campaign against child marriage. In Yemen, the story caused Parliament to discuss the issue and consider raising the minimum legal age of marriage for girls to 17 years.4 In Saudi Arabia, which has no legal minimum age for marriage, a draft law is now under discussion to set a minimum age for marriage of between 16 and 18. Until such a law is enacted, advocates are pressing for the Saudi government to ban notaries from legitimizing the marriages of girls under 18.5
References
- UNICEF, Early Marriage: Child Spouses (Florence, Italy: UNICEF Innocenti Research Centre: 2001).
- UNICEF, Progress for Children: A Report Card on Child Protection, Number 8, accessed at www.childinfo.org/files/Progress_for_Children-No.8_EN.pdf, on Feb. 23, 2010.
- Rhonda Smith et al., Family Planning Saves Lives, Fourth Edition (Washington, DC: Population Reference Bureau: 2009).
- Heather Murdock, “Child Brides in Yemen Seek Legal Protection,” Voice of America News, accessed at www1.voanews.com/english/news/Child-Brides-in-Yemen-Seek-Legal-Protection-83233392.html, on Feb. 1, 2010.
- Hugh Tomlinson, “12-Year-Old Saudi Girl in Divorce Battle With 80-Year-Old Husband,”Time Online, Feb. 9, 2010; and Asma Alsharif, “Saudi Rights Commission Seeks Divorce for Child Bride,” Reuters, Feb. 8, 2010.

